Defence engineering is a field that constantly evolves in response to technological advancements, driven by the need for enhanced security and strategic superiority. From the early invention of gunpowder to the sophisticated development of stealth aircraft, innovation has always been at the forefront of military advancements. Today, companies like Bendtech Defence are at the cutting edge, contributing to the emergence of new technologies that are reshaping the landscape of engineering. These innovations are transforming how nations protect their interests, maintain security, and prepare for future conflicts.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Defence Engineering
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has introduced significant changes across various sectors. The integration of AI into engineering is largely due to its ability to perform tasks traditionally requiring human intelligence, such as pattern recognition, language understanding, and problem-solving. AI has become indispensable in the development of autonomous weapons systems, which can identify and engage targets with minimal human intervention.
Autonomous systems powered by AI include unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs). These systems can conduct surveillance, reconnaissance, target recognition, and even direct engagement with adversaries during conflicts. Their ability to operate in dangerous environments without risking human lives offers a significant strategic advantage. Moreover, AI enhances cyber systems by detecting potential threats of cyberattacks that could go unnoticed by human operators. This capability is particularly important in the modern battlefield, where cyber warfare has become a critical component of national security.
Additive Manufacturing or 3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, offers substantial benefits in engineering. This technology allows for the creation of customized, complex, and lightweight parts with minimal waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods. 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize the production of military equipment, enabling faster and more flexible manufacturing processes.
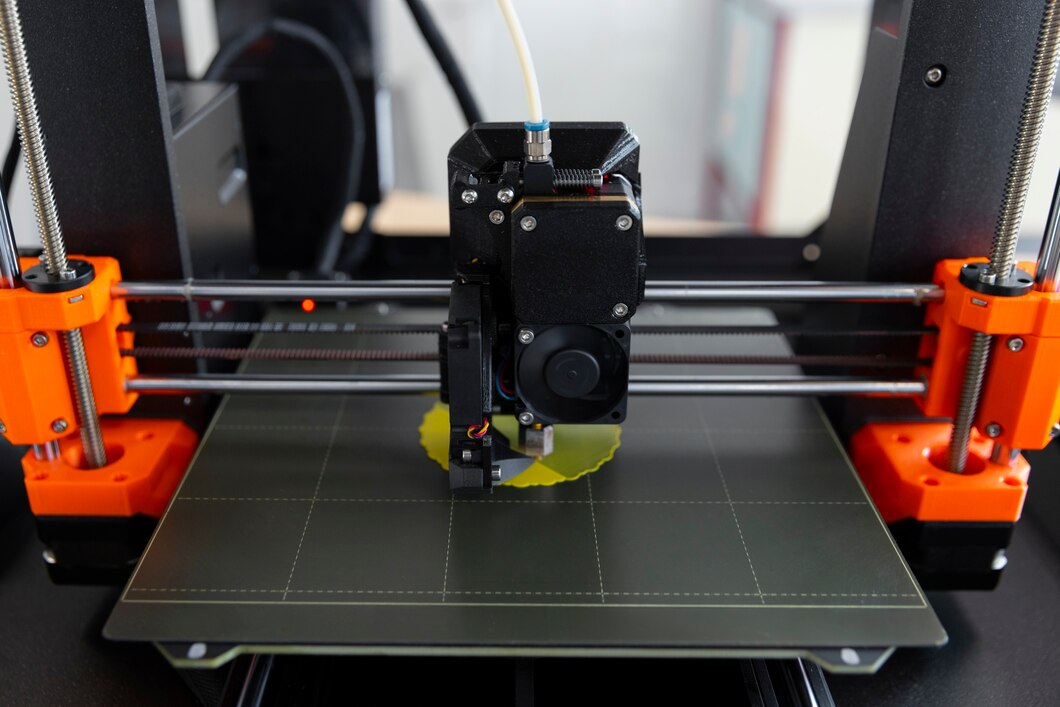
One of the major benefits of 3D printing is its capability to manufacture parts as needed, especially in field operations.. In combat or remote locations, the availability of spare parts can be a matter of life and death. 3D printers can produce necessary components on-site, reducing the logistics burden and ensuring rapid response times in equipment repair and replacement. This capability enhances the operational readiness of military forces, allowing them to maintain their equipment and vehicles in optimal condition even in challenging environments.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing, though still in its developmental stage, holds the potential to revolutionize defence engineering. Unlike traditional computers that operate on bits (which can be either 0 or 1), quantum computers use quantum bits or qubits, which can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously. This ability to perform multiple calculations at once gives quantum computers a significant advantage in processing power.
In this context, quantum computing could drastically improve cryptography, enabling the development of quantum encryption techniques for secure communications. Quantum encryption is expected to be virtually unbreakable, offering a level of security that is critical for protecting sensitive military communications and data. Additionally, quantum computing could enhance the modeling and simulation of warfare strategies, allowing for more accurate predictions of enemy movements.
Cyber Defence and Information Technologies
Cybersecurity has become a central focus in engineering, driven by the increasing reliance on digital information and communication systems. These systems are integral to various operations, managing everything from communications to surveillance and logistics. As a result, protecting them from cyber threats is essential to maintaining security.
Countries around the world are investing heavily in technologies to protect their infrastructure against cyberattacks, such as ransomware, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Advances in encryption technologies, intrusion detection systems, and firewalls have become key components of cybersecurity strategies, with AI-driven solutions showing particular promise for identifying and responding to threats in real-time.
Hypersonics
Hypersonic technology, which involves flight at speeds exceeding Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound), represents one of the most significant advancements in modern engineering. Hypersonic weapons can travel at incredible speeds and at varying altitudes, making them difficult to detect and intercept with existing systems. This capability provides a significant strategic advantage, enabling nations to strike targets globally with unprecedented speed and precision.
The development of hypersonic weapons has led to a new arms race, with countries striving to achieve technological superiority in this domain. Hypersonic missiles, for example, can bypass traditional missile systems, rendering them less effective. As a result, engineers are working on developing new countermeasures to protect against hypersonic threats.
Final Thoughts
Emerging technologies are redefining the possibilities in engineering, transforming the sector into a more agile, resilient, and effective force. The integration of AI, quantum computing, additive manufacturing, cyber defence technologies, and hypersonics is creating a new era of capabilities. While these advancements offer immense potential, they also present significant challenges, particularly in terms of ethical considerations and the need to overcome technological barriers.

